[프로그래머스] 전력망을 둘로 나누기
코딩테스트 연습 - 전력망을 둘로 나누기 문제 바로가기
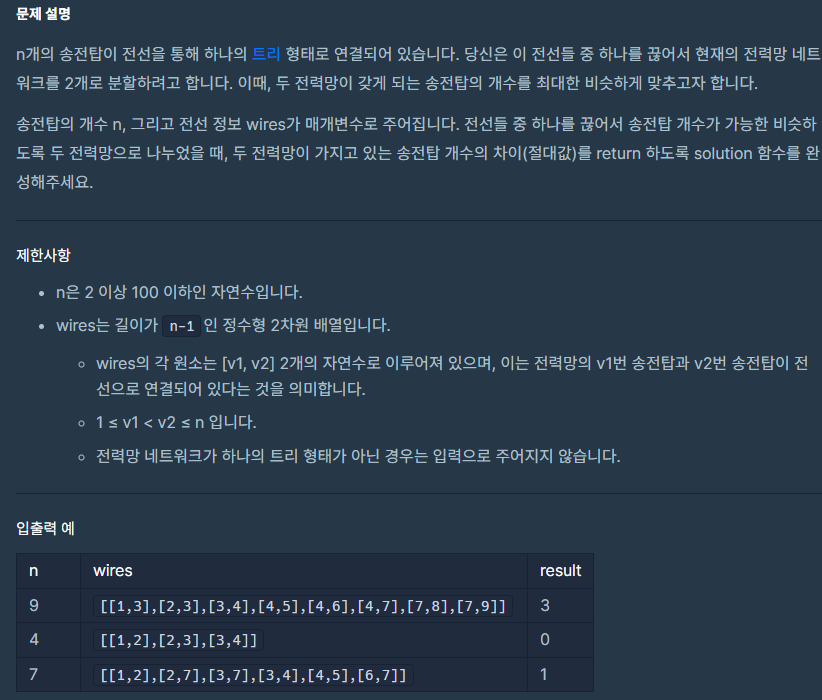
문제 설명
전체 전력망을 2개의 전력망으로 나눴을 때, 두 전력망(그래프)의 노드 개수 차이가 가장 최소가 되는 값을 반환해야 합니다.
따라서 그래프에 이어진 노드 개수 를 빠르게 파악하는 것이 중요하기 때문에
그래프 탐색 중 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)를 사용했습니다.
그리고 전력망을 나누기 위해 2중 반복문으로 한 원소씩 빼서 탐색을 진행했습니다.
마지막으로 BFS 에서 탐색 시작 노드를 알기 위해
반복문으로 그래프가 연결되어 있는 노드를 찾아 시작 노드로 선택했습니다.
제출 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int BFS(int n, vector<vector<int>> graph) {
int start_node;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if(false == graph[i].empty()) {
start_node = i;
break;
}
}
queue<int> q;
q.push(start_node);
bool* visited = new bool[n + 1];
fill(visited, visited + n + 1, false);
visited[start_node] = true;
int node_count = 1;
while(false == q.empty()) {
int curr = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int next : graph[curr]) {
if(false == visited[next]) {
visited[next] = true;
q.push(next);
node_count += 1;
}
}
}
return node_count;
}
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> wires) {
int answer = 2e9;
for(auto remove : wires) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(n + 1, vector<int>());
for(auto edge : wires) {
if(edge != remove) {
graph[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);
graph[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);
}
}
int first_node_count = BFS(n, graph);
int second_node_count = n - first_node_count;
answer = min(abs(first_node_count - second_node_count), answer);
}
return answer;
}
제출 결과
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.